How to manage folder permissions with PowerShell
Managing files and folder permissions it's a time consuming process. When you are trying to apply level of permissions in a Fileserver with hundred of folders might take you days. Especially when it's already in production.
PowerShell can reduce the time of this process and make it easier. Probably when you have to manage or update folder permissions in a Fileserver with hundred or thousand of folders.
I spent few hours a day while testing different scenarios that we are facing when we should manage or update folder permissions.
NTFS File and Folder Permissions
Before start to explain how to get folder permissions with PowerShell , check folder permissions with PowerShell or anything let's remember the NTFS file and folder permissions.
The following tables with the basic and advance permissions are copied from a link of the Microsoft Learn.
The table describe the basic permissions of a folder.
|
Permission |
Meaning for Folders |
Meaning for Files |
|---|---|---|
|
Read |
Permits viewing and listing of files and subfolders |
Permits viewing or accessing of the file's contents |
|
Write |
Permits adding of files and subfolders |
Permits writing to a file |
|
Read & Execute |
Permits viewing and listing of files and subfolders as well as executing of files; inherited by files and folders |
Permits viewing and accessing of the file's contents as well as executing of the file |
|
List Folder Contents |
Permits viewing and listing of files and subfolders as well as executing of files; inherited by folders only |
N/A |
|
Modify |
Permits reading and writing of files and subfolders; allows deletion of the folder |
Permits reading and writing of the file; allows deletion of the file |
|
Full Control |
Permits reading, writing, changing, and deleting of files and subfolders |
Permits reading, writing, changing and deleting of the file |
The table describe the advance permissions of a folder
|
Full Modify |
Execute |
Read & Contents |
Folder Read |
List Write |
Special Permissions |
Control |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Traverse Folder / |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
|
Execute File |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
List Folder /Read Data |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
Read Attributes |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
Read Extended |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
|
Attributes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Create Files / |
X |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
Write Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Create Folders / |
X |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
Append Data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Write Attributes |
X |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
Write Extended |
X |
X |
|
|
|
X |
|
Attributes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delete Subfolders |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
and Files |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Delete |
X |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
Read Permissions |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
X |
|
Change Permissions |
X |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Take Ownership |
X |
|
How to get folder permissions with PowerShell
First of all let's see how to get the folder permissions with the PowerShell commands.
I have created a folder in C:\ with Folder Name C:\Myfolder
- Open a PowerShell as Administrator
- Run the command
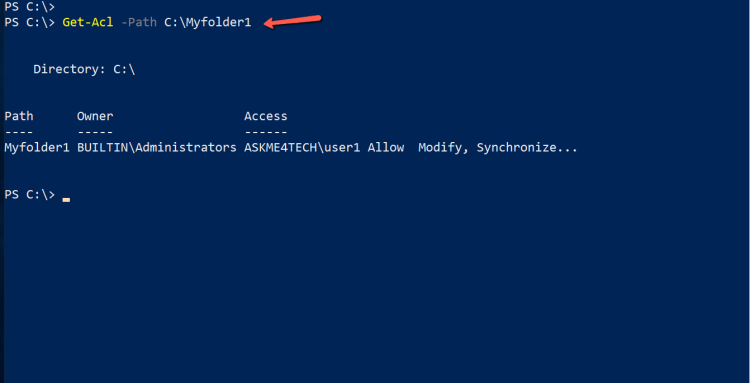
Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1
- As you can see the display it's not help.
- So after some research i found the following.
- If you run the following command it will display all the options that you can use with the Get-Acl
Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1 | Select *
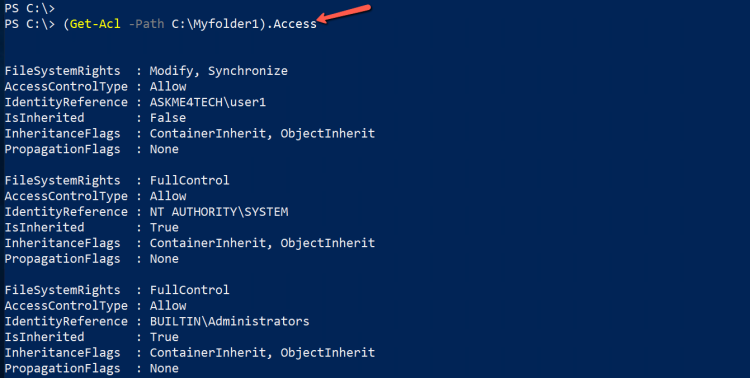
- Use the Access and Type (Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1).Access
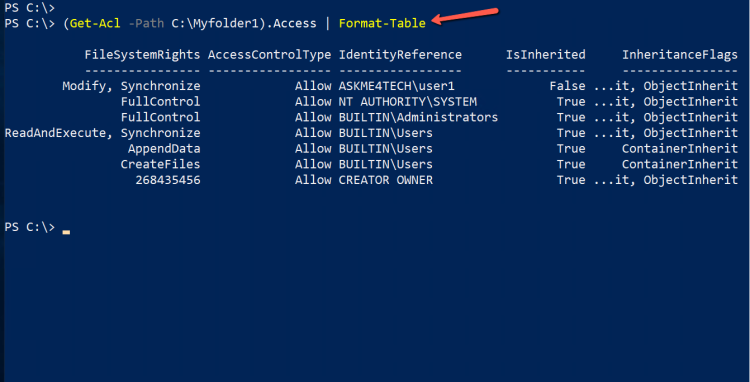
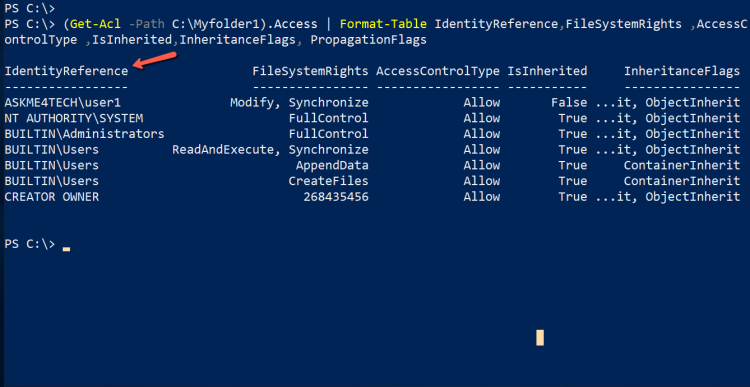
- We can do it much better if we will use the Format-Table
(Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1).Access | Format-Table
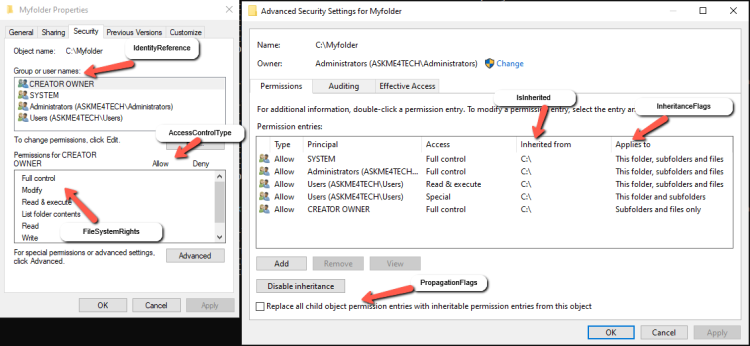
- Now let's take a look how can map this columns with the Security Tab of a Folder
- IdentityReference = It is the Group or the user name that you give the access.
- FileSystemRights = Are the Permissions as you will see it in the Security Tab of the folder
- AccessControlType = The Allow or Deny access
- IsInherited = If the permissions are inherited.
- InheritanceFlags = It's the Applies To as you can see it in Advanced Security Settings.
- ContainerInherit = When applies in any of the options in Applies To except from the Files only.
- ObjectInherit = When applies in the option Files only in Applies To
- PropagationFlags = How inheritance is propagated to the child objects
- If we would like to tp change the order of the columns we can run the command as follow.
(Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1).Access | Format-Table IdentityReference,FileSystemRights ,AccessControlType ,IsInherited,InheritanceFlags, PropagationFlags
How to change folder permissions with PowerShell
This time the steps are more complicated to do it with PowerShell for a single or 2 folders. However , it's faster when you need to change hundred of folders especially with the same permissions.
Let's see it in practice.
- Open the PowerShell.
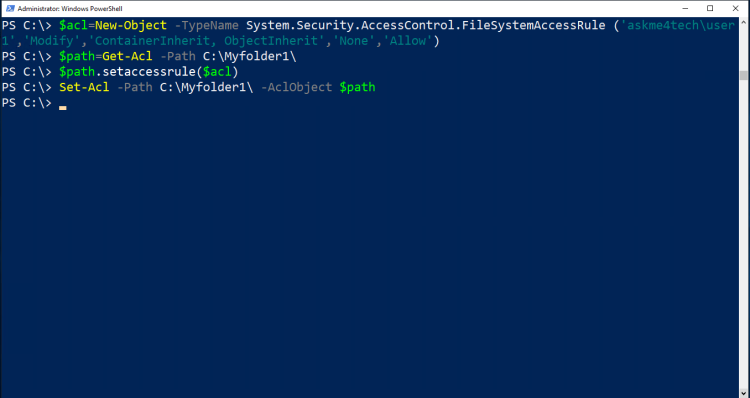
- Type the following script to give in user askme4tech\user1 Modify permissions in the folder C:\Myfolder1.
$path=Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1\
$acl=New-Object -TypeName System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule ('askme4tech\user1','Modify','ContainerInherit, ObjectInherit','None','Allow')
$path.setaccessrule($acl)
Set-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1\ -AclObject $path
- Let's explain what we are doing here.
- In the first line $path=Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1\ we save the folder path in a variable path because we need to pass the security permissions later.
- The second line it's the more interesting. We create a new object with the FileSystemAccessRule class which has 5 parameters
- IdentityReference = It is the Group or the user name that you give the access.
- FileSystemRights = Are the Permissions as you will see it in the Security Tab of the folder
- AccessControlType = The Allow or Deny access
- InheritanceFlags = It's the Applies To as you can see it in Advanced Security Settings.
- ContainerInherit = When applies in any of the options in Applies To except from the Files only.
- ObjectInherit = When applies in the option Files only in Applies To
- PropagationFlags = How inheritance is propagated to the child objects
- In the next line we are passing the new security permissions to the setaccessrule() method
- The last line apply the folder permission to the folder with the Set-Acl
- This is the order that you should keep to apply new permissions or modify existing one with the PowerShell.
How to copy permissions to a new object with Get-Acl
Copy permissions to a new object with PowerShell it's very fast and reduce the time that we need to do it with GUI.
For the example I have create a new folder in C:\ with folder name myFolder2.
Let's see how can do it.
- Go in C:\ and type dir to verify that we have both folders (Myfolder1 and Myfolder2) for the example.
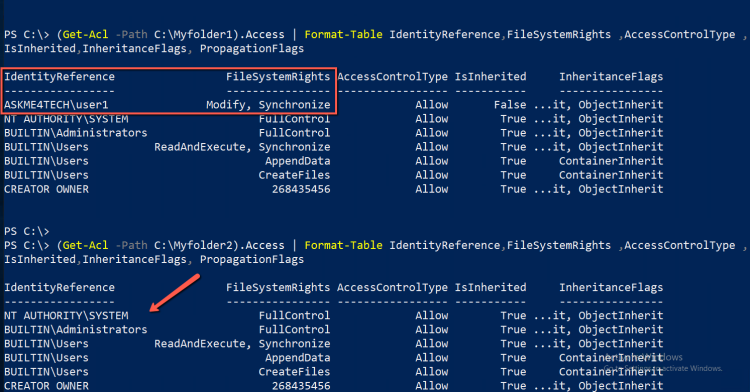
- Get the folder permissions from both folders
- As you can see in the folder Myfolder2 user2 don't have access.
- Type and run the following command to copy the folder permissions from Myfolder1 to Myfolder2
Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1\ | Set-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder2\
- Now get the folder permissions for the folder Myfolder2. As you can see all the permissions from myfolder1 copied to myfolder2
(Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder2).Access | Format-Table IdentityReference,FileSystemRights ,AccessControlType ,IsInherited,InheritanceFlags, PropagationFlags
With one line of PowerShell you can copy permissions from one folder to another instead of GUI that you need lot of steps for every permission.
How to remove permissions with PowerShell
If you want to remove permissions from a folder or file the commands are also the same as change folder permissions.
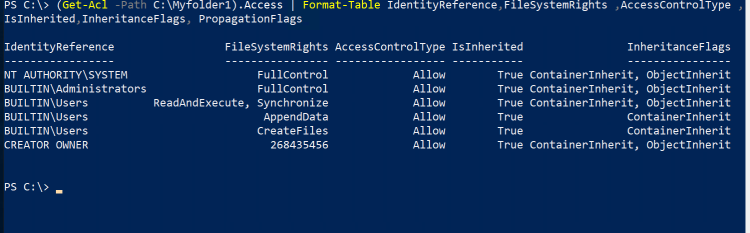
- Type the following commands to remove the permissions from user1 in folder Myfolder1.
- The only difference is in line 3 which use the removeaccessrule() method instead of the setaccessrule() method.
$path=Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1\
$acl=New-Object -TypeName System.Security.AccessControl.FileSystemAccessRule ('askme4tech\user1','Modify','ContainerInherit, ObjectInherit','None','Allow')
$path.removeaccessrule($acl)
Set-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1\ -AclObject $path
- If you get the folder permissions you will see that the user 1 removed from the security permissions
(Get-Acl -Path C:\Myfolder1).Access | Format-Table IdentityReference,FileSystemRights ,AccessControlType ,IsInherited,InheritanceFlags, PropagationFlags
Manage security permissions with PowerShell it's very easy and much faster from GUI. You can reduce your time of tasks that related with change,add or remove permissions of multiple folder using the PowerShell.
Have a nice weekend !!.